Implementation and extended Replication: Unbiased Look at Dataset Bias
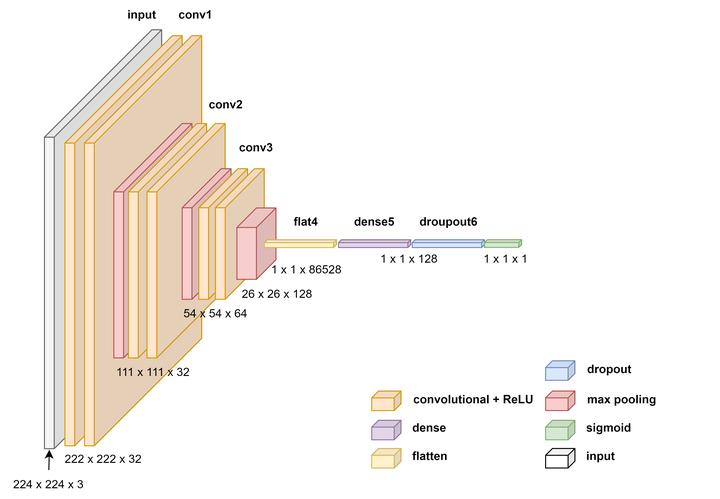 CNN Architecture used for image classification
CNN Architecture used for image classification
Introduction
The project revolves around understanding dataset bias in image classification tasks, inspired by the seminal work of Torralba and Efros (2011). It explores biases in datasets such as Caltech101, MSRC, and VOC-2007 using traditional methods like Histogram of Gradients (HOG) with Support Vector Machines (SVM) and modern Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN).
Literature Review
Biases in Image Datasets
-
Selection Bias: Occurs during dataset creation, leading to overrepresentation or underrepresentation of certain categories (e.g., too many racing cars).
-
Framing Bias: Arises from how images are composed or presented (e.g., all “car_side” images in Caltech101 are black and white).
-
Label Bias: Results from errors in image labeling or ambiguous semantic categories, impacting algorithm performance.
Methods
Datasets Description
-
Caltech101: Created in 2003 with 9000 images across 101 categories, including “car_side” images.
-
MSRC: Microsoft Research Cambridge dataset with around 4300 labeled images.
-
PASCAL VOC-2007: Contains around 5000 annotated images with 20 object classes, including “car”.
Preprocessing
- Standardized all images to 224x224 pixels.
- Applied binary labeling for car versus non-car images across datasets.
SVM Approach
- Implemented HOG feature extraction followed by SVM classification.
- Used 2-way SVM for binary classification.
- Examined F1 scores for cross-dataset generalization, observing significant performance drops.
CNN Approach
- Developed a CNN architecture with convolutional layers (32, 64, 128 filters), max-pooling layers, dense layers (128 neurons), and dropout layers.
- Trained using Adam optimizer with binary cross-entropy loss.
- Implemented Early Stopping to mitigate overfitting.
- Evaluated F1 scores and observed performance degradation across different datasets.
Findings
SVM Results
- Demonstrated lower F1 scores in cross-dataset testing, indicating susceptibility to dataset biases.
- Highlighted the need for multi-label datasets to improve classification accuracy.
CNN Results
- Showed similar performance trends as SVM but with different magnitudes of performance drops.
- Noted instances of complete failure (F1 score of 0) in specific cross-dataset tests, suggesting deeper biases or model limitations.
Discussion
- Discussed limitations such as computational constraints affecting model capacity.
- Proposed future research directions including using more recent datasets and advanced object detection models.
- Reflected on methodological biases introduced by the algorithms themselves, impacting bias assessment.
Authors
- Christian Hobelsberger
- Erwin Spoelstra
- Sanjit Dasgupta